Chapter 5
3D Modeling Services
3D modeling is the backbone of every CGI workflow. It covers all types of product rendering, animation, configurators, AR, and VR. No matter how advanced the final result looks, everything starts with a clean, accurate, well-optimized 3D model. If the model is incorrect, even the most advanced lighting, materials, or animation will fail to look realistic.
A professional 3D model can be built from almost any input: photographs, CAD drawings, technical blueprints, video references, 360° walkarounds, or even 3D scans. What matters is translating these sources into geometry that meets the needs of rendering or real-time engines.
Just as importantly, models for photorealistic rendering and models for real-time interaction (AR/VR/web) are two very different categories.
• Rendering models prioritize micro-details and realism. • Real-time models prioritize polygon efficiency and speed.
This guide explains all major modeling types, categories, complexity levels, reference requirements, outputs, software, and the complete workflow used at CGIFurniture.
Types of 3D Modeling
Below are the essential modeling types used in product visualization, along with examples, applications, and key benefits.
Low-poly Modeling
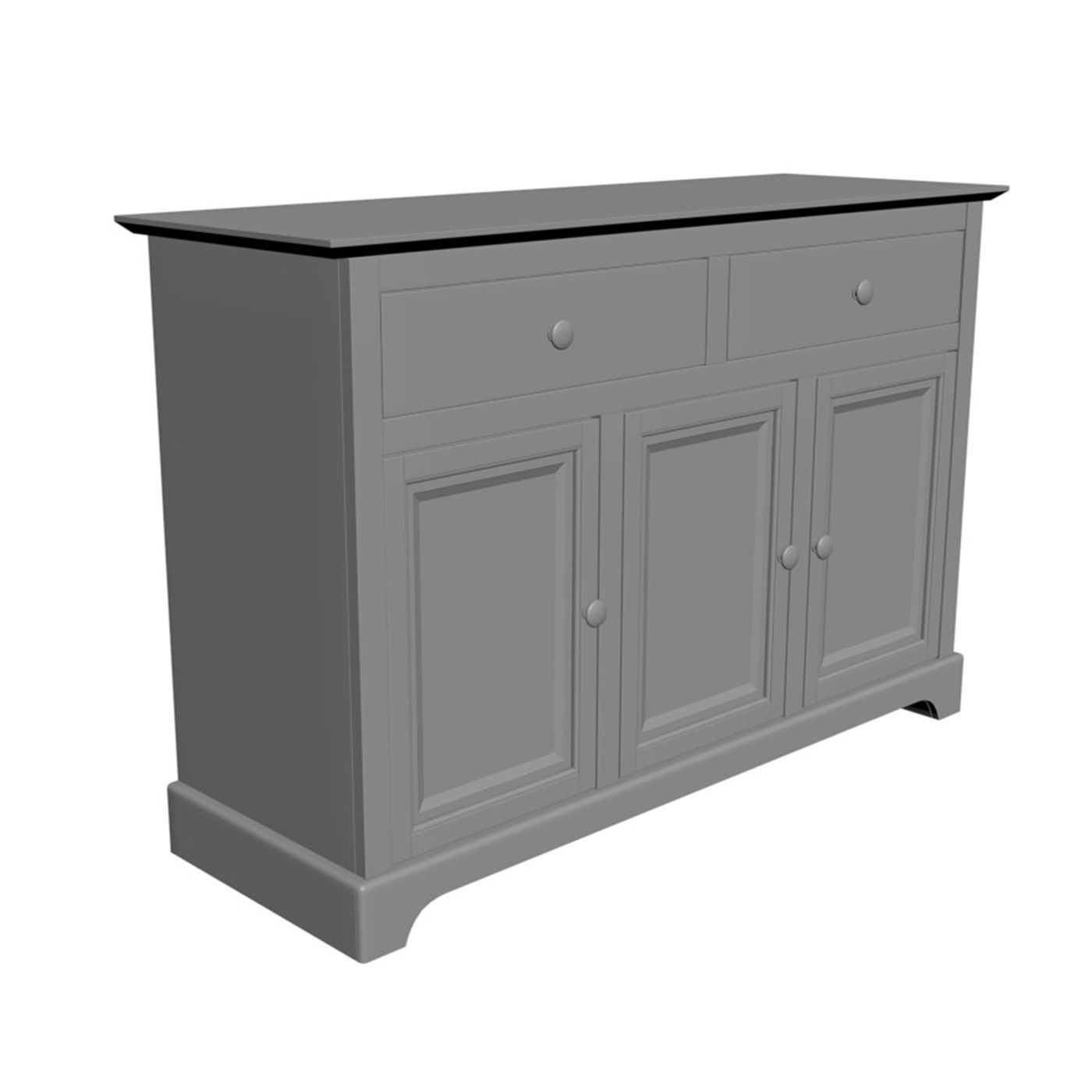

Examples: • Simple chairs for configurators • Basic light fixtures • Accessories like baskets, trays, and minimalistic décor
Where it’s used: • AR apps • Web configurators • 360° interactive product viewers • Mobile experiences • Real-time engines (Unreal, Unity)
Key benefits: • Fast loading and smooth browser performance • Minimal polygon count • Ideal for animation and motion in real-time • Easy to scale for large catalogs
High-poly Modeling

Examples: • Sofas with stitched seams • Premium armchairs with quilting • Metal structures with chamfers and micro-details
Where it’s used: • Photorealistic rendering (V-Ray, Corona) • Product feature shots • Advertising and lifestyle imagery • Close-up shots
Key benefits: • Maximum realism • Ability to show fabric folds, stitching, bevels, dents, and curves • Support for micro-displacement and subdivision
CAD-based Modeling
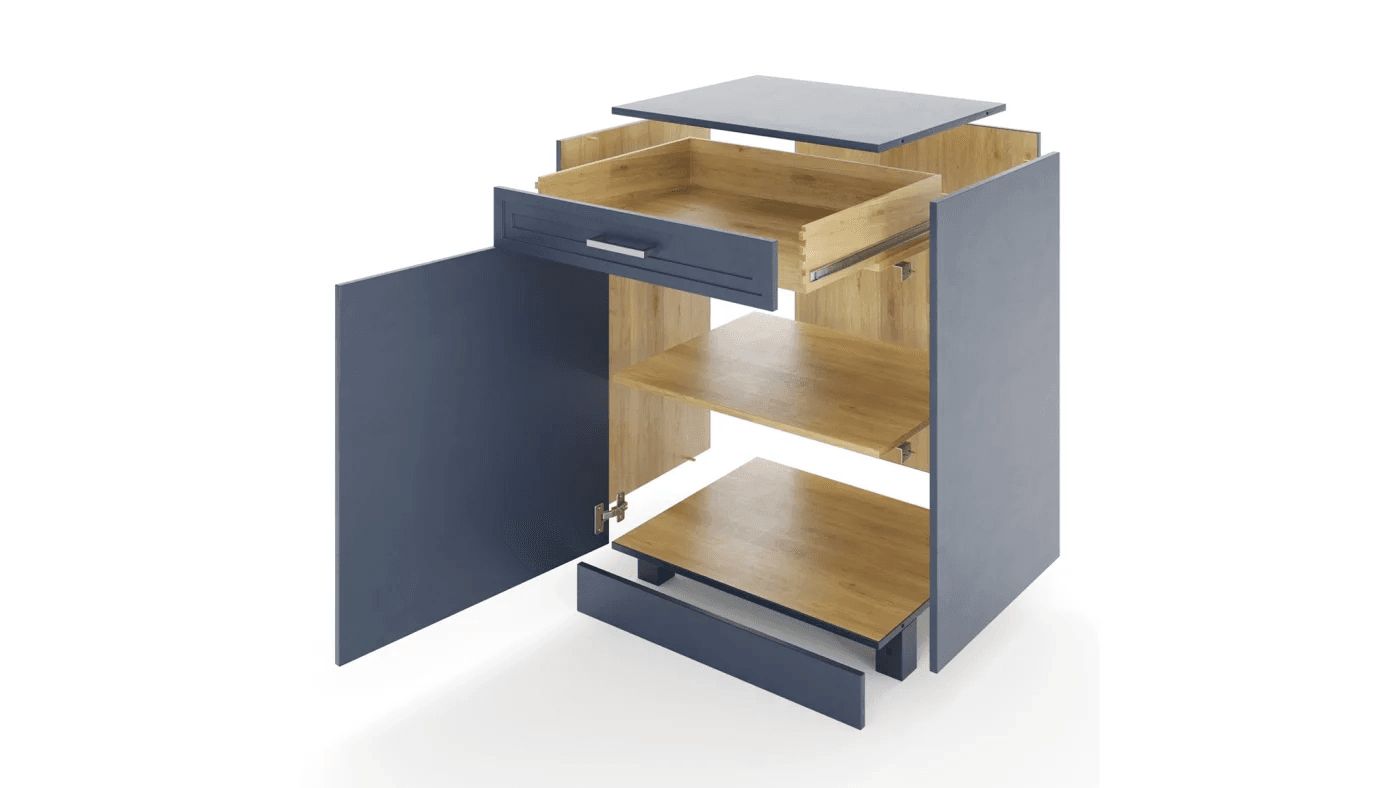

Examples: • Hardware and fittings • Technical components • Faucets, mixers, appliances • Industrial objects with precise tolerances
Where it’s used: • Exploded-view diagrams • Technical presentations • Manufacturing visualization • Adaptation for rendering
Key benefits: • High accuracy • Perfect engineering geometry • Ability to preserve original dimensions
3D Retopology

Examples: • Converting dense CAD models into clean versions • Preparing 3D scans for rendering • Rebuilding models for AR or animation
Where it’s used: • Real-time engines • AR/VR • Product animations • Web configurators
Key benefits: • Mid-poly models suitable for real-time • Smoother surface flow • Drastically reduced file size • Cleaner UVs and easier texturing
Model Categories
Each product type has its own nuances and technical requirements.
Furniture (Hard-Surface)

Examples: tables, cabinets, metal frames.
Nuances: • Correct chamfers • Clean geometry and precise angles • Realistic wood and metal behavior
Upholstered Furniture
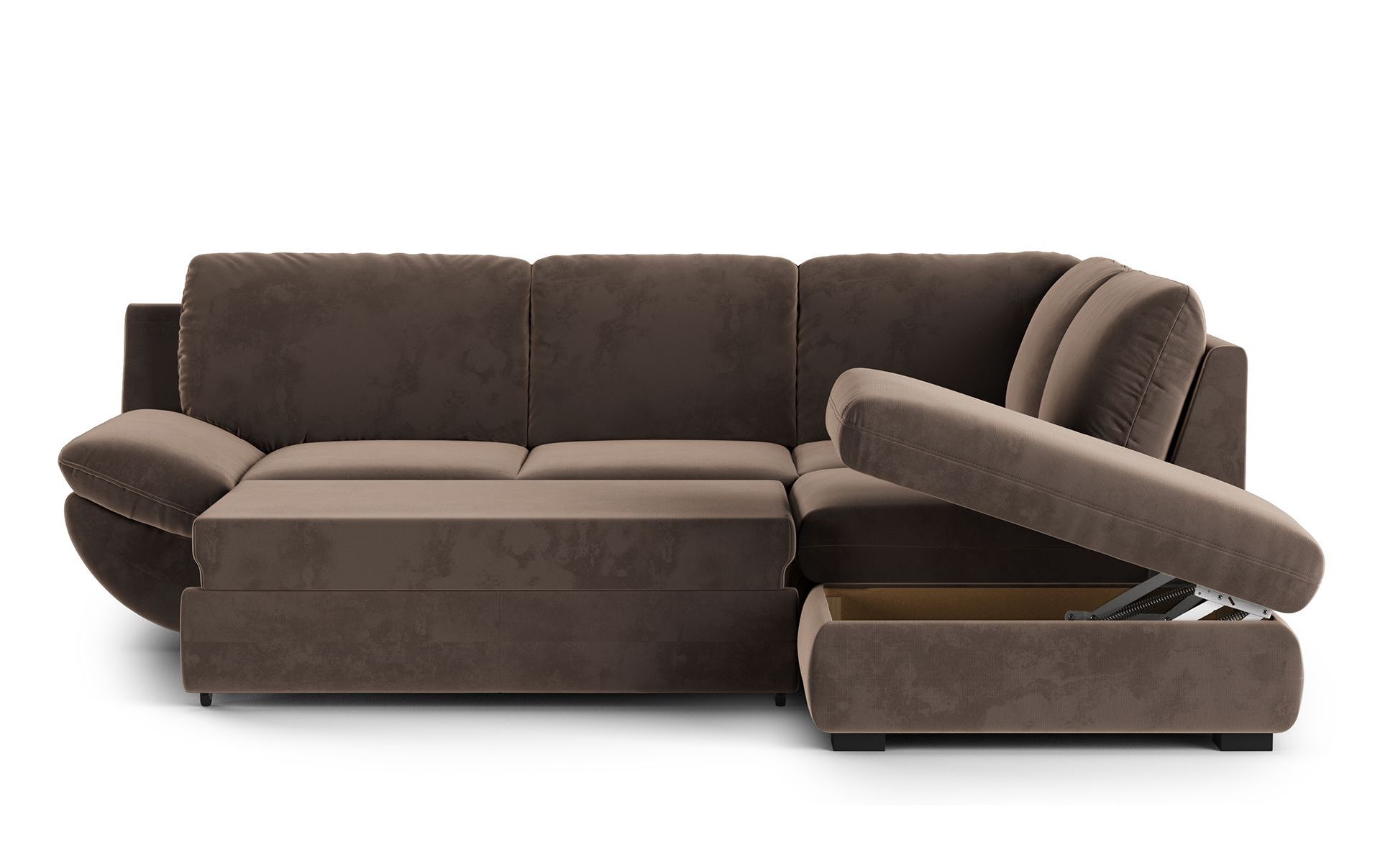

Examples: sofas, poufs, armchairs.
Nuances: • Cloth simulation • Proper cushion deformation • Natural wrinkles and seams
Lighting
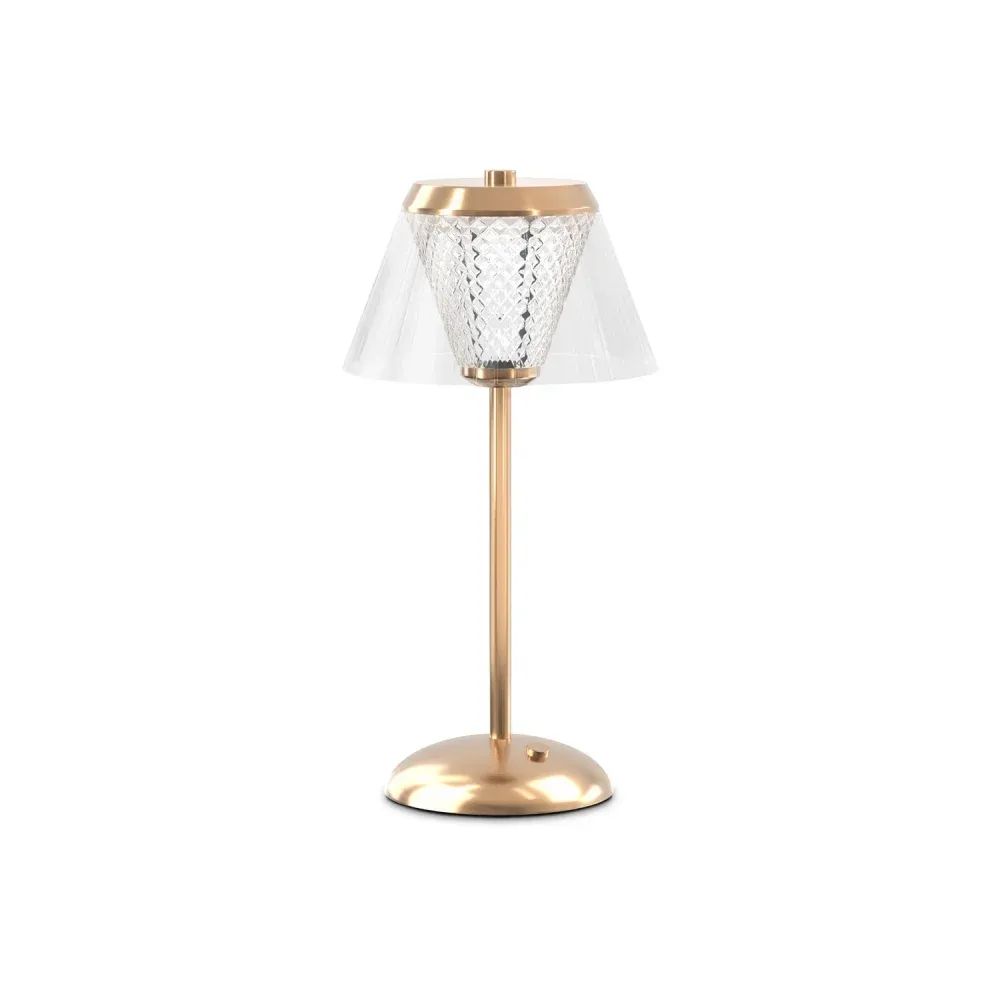

Examples: pendants, floor lamps, sconces.
Nuances: • Transparent and translucent materials • Internal lamp structure • Correct refraction
Décor & Accessories
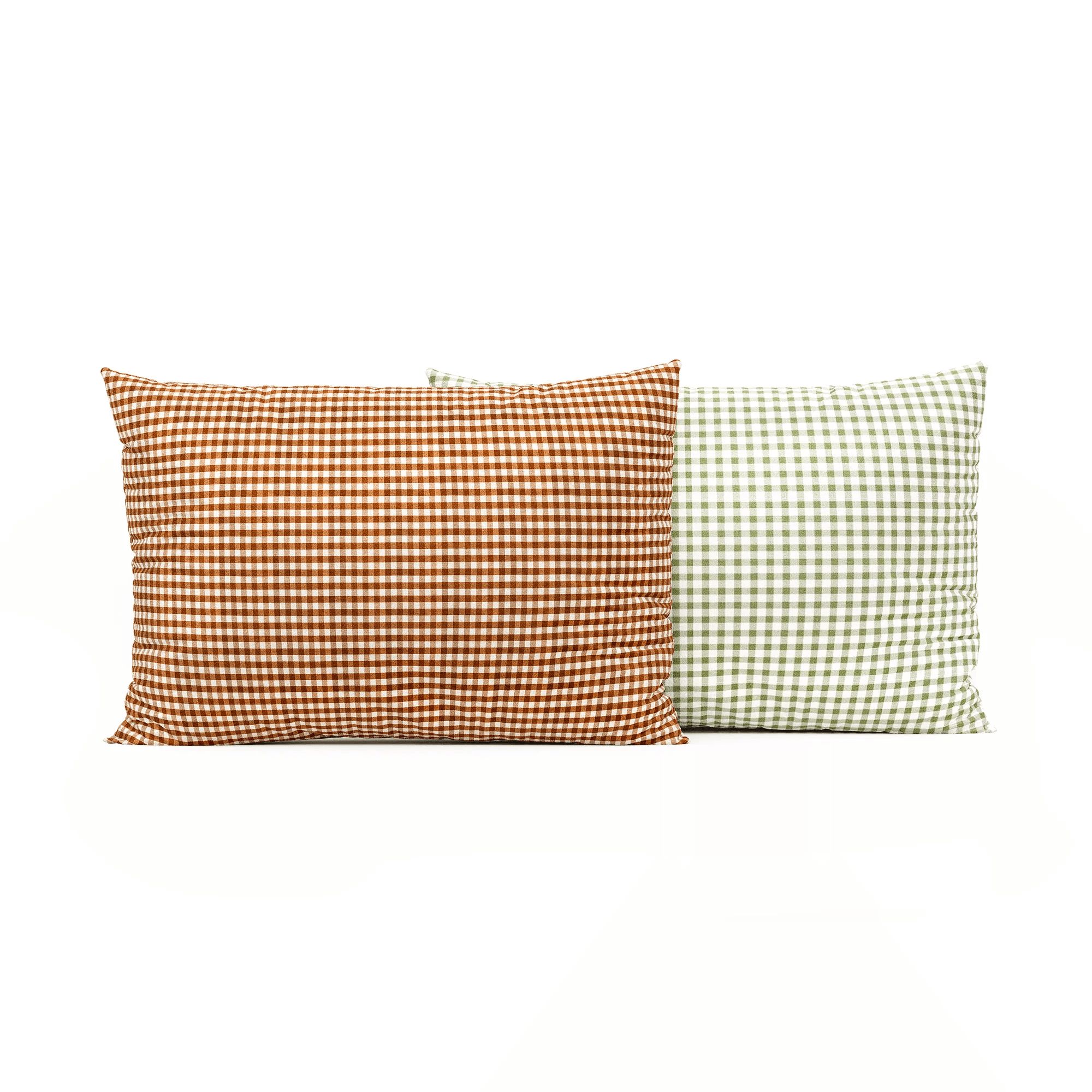

Examples: vases, bowls, organic shapes.
Nuances: • Complex curves • Glass and ceramics • Imperfections for realism
Technical / Industrial Items
Examples: fasteners, connectors, fittings.
Nuances: • Engineering geometry • High precision • Small but important details
Outdoor Furniture
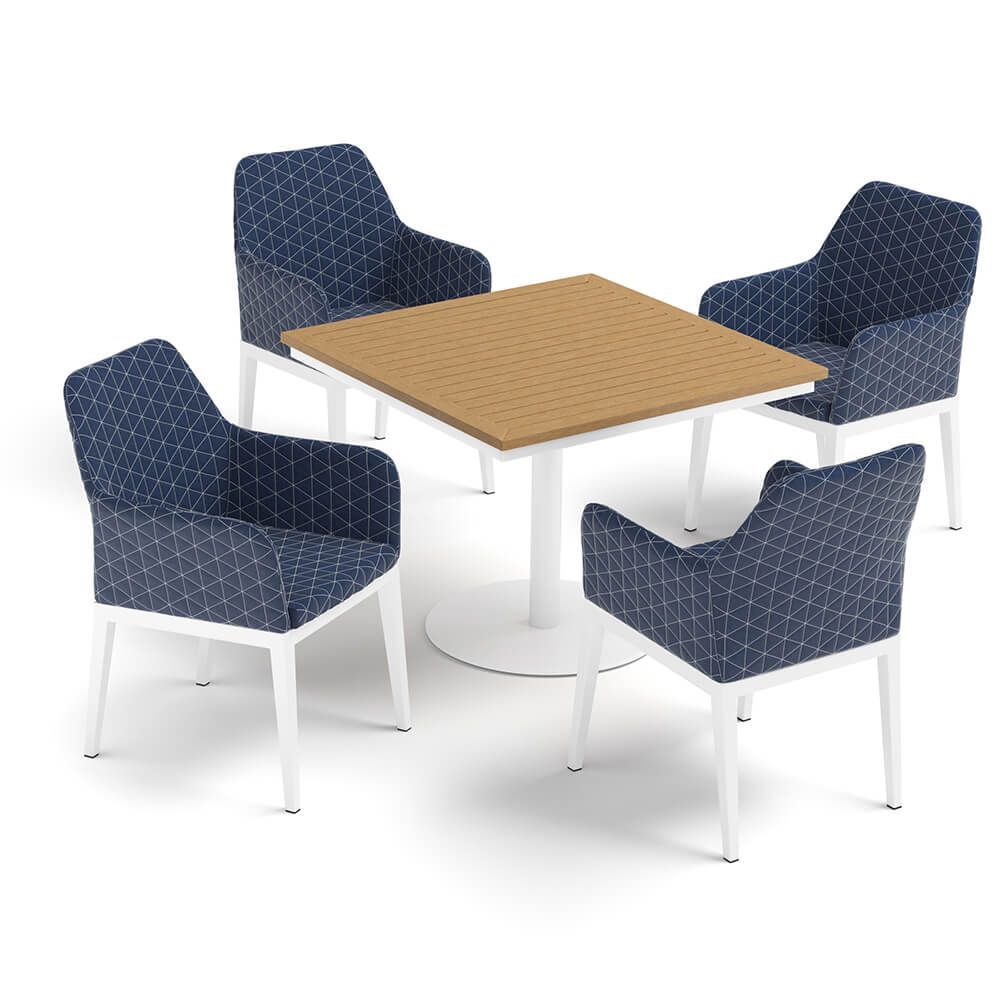

Examples: wicker items, metal frames, stone tops.
Nuances: • Natural material variation • Non-perfect shapes • Weathering effects
Appliances

Examples: kettles, microwaves, ovens.
Nuances:
- Plastic + metal combinations
- LED indicators
- Glossy surfaces and tight tolerances
Levels of Modeling Complexity
Below is a clear breakdown of the four main levels of furniture 3D modeling, based on CGIFurniture’s internal standards. Understanding these categories will help you identify the right model type for your product and plan your CGI budget more accurately.
1. Simple Models
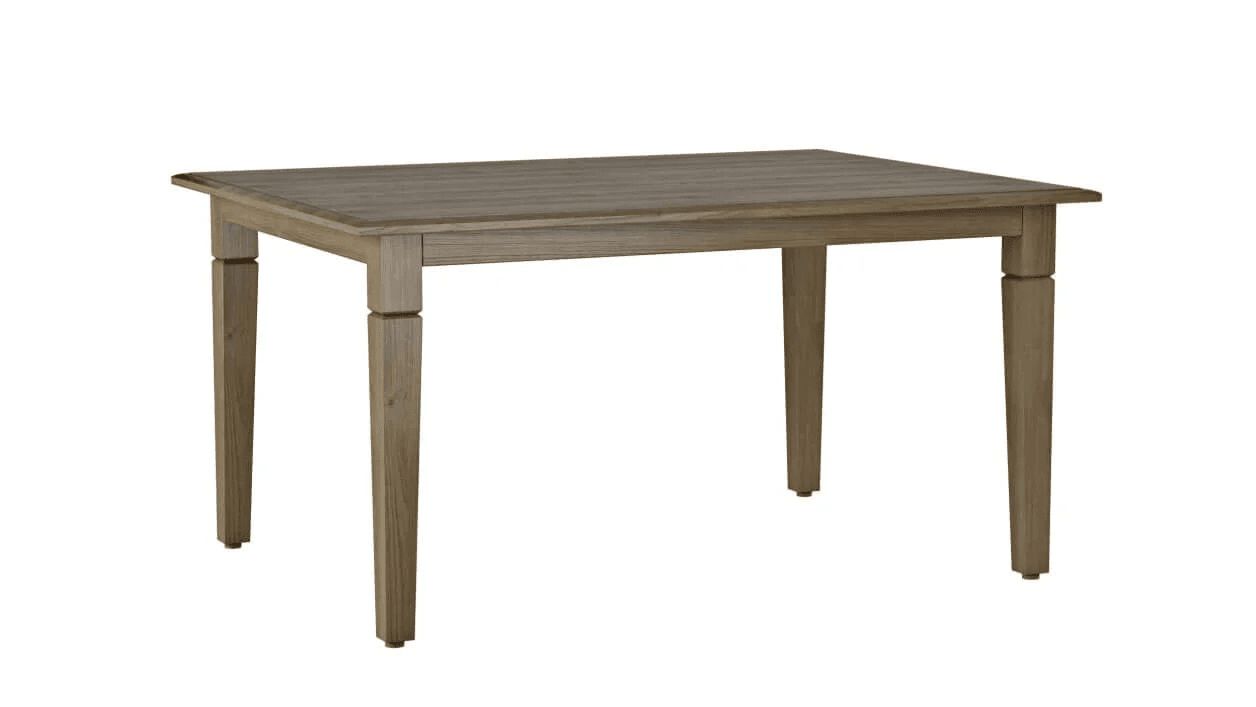

What they are: Simple models feature minimal geometry and very few details. They are built from basic shapes such as cubes, spheres, cylinders, and work perfectly for straightforward furniture items such as basic chairs, tables, benches, or simple shelving.
Characteristics:
- No seams, stitches, or fittings
- No complex texturing
- Often created from ready-made geometry and standard texture maps
- Fastest and easiest to produce
- Typical production time: ~1 working day
- Price range: ~$40–$60
- When to choose this level: For minimalist products with clean geometry and no ornamental elements. Ideal for quick prototyping or basic catalog imagery.
2. Medium Complexity Models

What they are: Medium-level models include furniture with slightly more nuanced geometry — still fairly simple, but featuring more components and visible details.
Examples: Sideboards, bedside tables, TV consoles, chests of drawers, and similar cabinet pieces.
Characteristics:
- Moderate amount of decorative elements
- Simple fittings
- Common and uncomplicated textures
- Suitable for minimalistic or modern designs
- Typical production time: ~1 working day
- Price range: ~$80–$120
- When to choose this level: For furniture with clean lines but a bit more structural complexity. Perfect for most catalog-ready models.
3. Complex Models
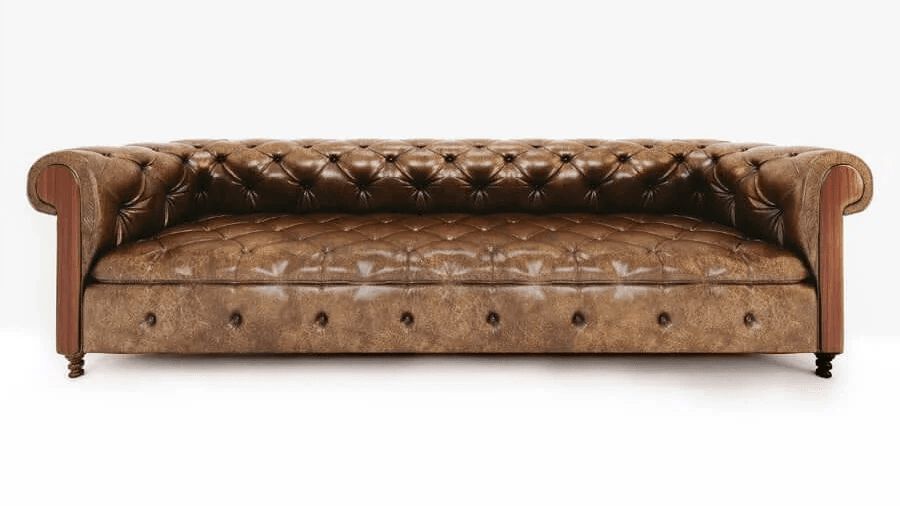

What they are: This tier covers furniture that requires intricate geometry, rich textures, and precise detailing.
Examples: Chesterfield sofas, upholstered armchairs, refined cabinetry, or furniture made of premium materials.
Characteristics:
- Detailed stitching, quilting, and fittings
- Challenging textures (leather, silk, unique woods, stone patterns)
- May require retopology in 3ds Max to optimize geometry for smooth performance
- Suitable for real-time rendering, AR/VR, configurators, and 360° viewers (if requested)
- Typical production time: ~2 working days
- Price range: ~$140–$200 When to choose this level: When the product has elaborate detailing or when the 3D model needs to be optimized for interactive digital experiences.
4. Highly Complex Models
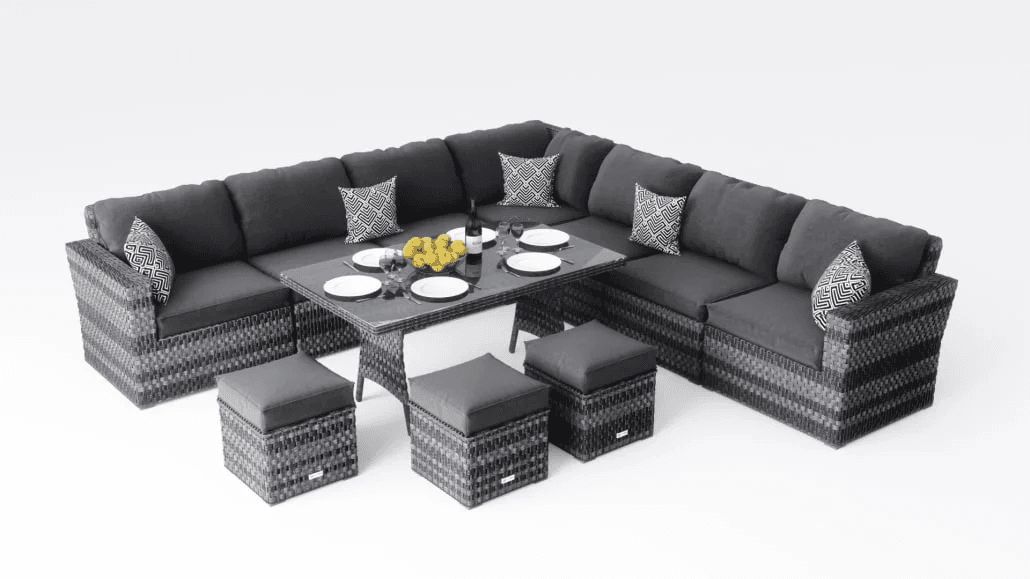

What they are: The top tier is used for furniture sets, multi-element compositions, or designs with extreme levels of sophistication.
Examples: Intricate furniture collections, items with carving, weaving, ornate materials, or many small components.
Characteristics:
- Large number of individual parts
- Extensive custom texturing and material creation
- Often requires retopology
- Each element is built with a fully customized approach
- Most time-consuming and detail-heavy modeling process
- Typical production time: ~2 working days (sometimes more, depending on set size)
- Price range: ~$220–$400
- When to choose this level: For luxury furniture brands, high-end marketing, or any product where visual realism and material accuracy are critical.
Factors Affecting Complexity
- Availability of CAD files or dimensions — the more accurate the references, the faster the workflow.
- Reference gaps — missing angles or low-quality photos increase complexity.
- Rigging requirements — hinges, openings, sliding parts, mechanisms.
- Material complexity — intricate textures, fabrics, patterns.
Reference Requirements
To create an accurate model, ideal references include:
- 360° video walkarounds
- Exact dimensions (height, width, depth)
- Close-ups of materials and details
- Finish options (colorways, hardware variations)
- Technical drawings or CAD if available
Accurate data reduces revisions and ensures scale precision.
Output

CGIFurniture provides models suitable for all pipelines:
High-poly (V-Ray / Corona)
- For photorealistic rendering
- Maximum details and displacement
Mid-poly (Unreal / Unity)
- Balanced for configurators and animations
Low-poly (AR / GLB / USDZ)
- Optimized for mobile and web
- Quick loading and smooth interaction
UV Mapping
- Unwrap required for realistic materials
- Essential for PBR texturing
STEM-ready geometry
- Precise enough for manufacturing visualization
- Clean, accurate topology
How a 3D Model Is Made
Let’s look at the 3D modeling workflow based on CGIFurniture’s pipeline.
Step 1: Studying the Assignment
- Analyzing photographs, CAD, videos, or scans
- Identifying missing references
- Defining model complexity and final output requirements
- Checking materials and colorways
Step 2: Building Geometry
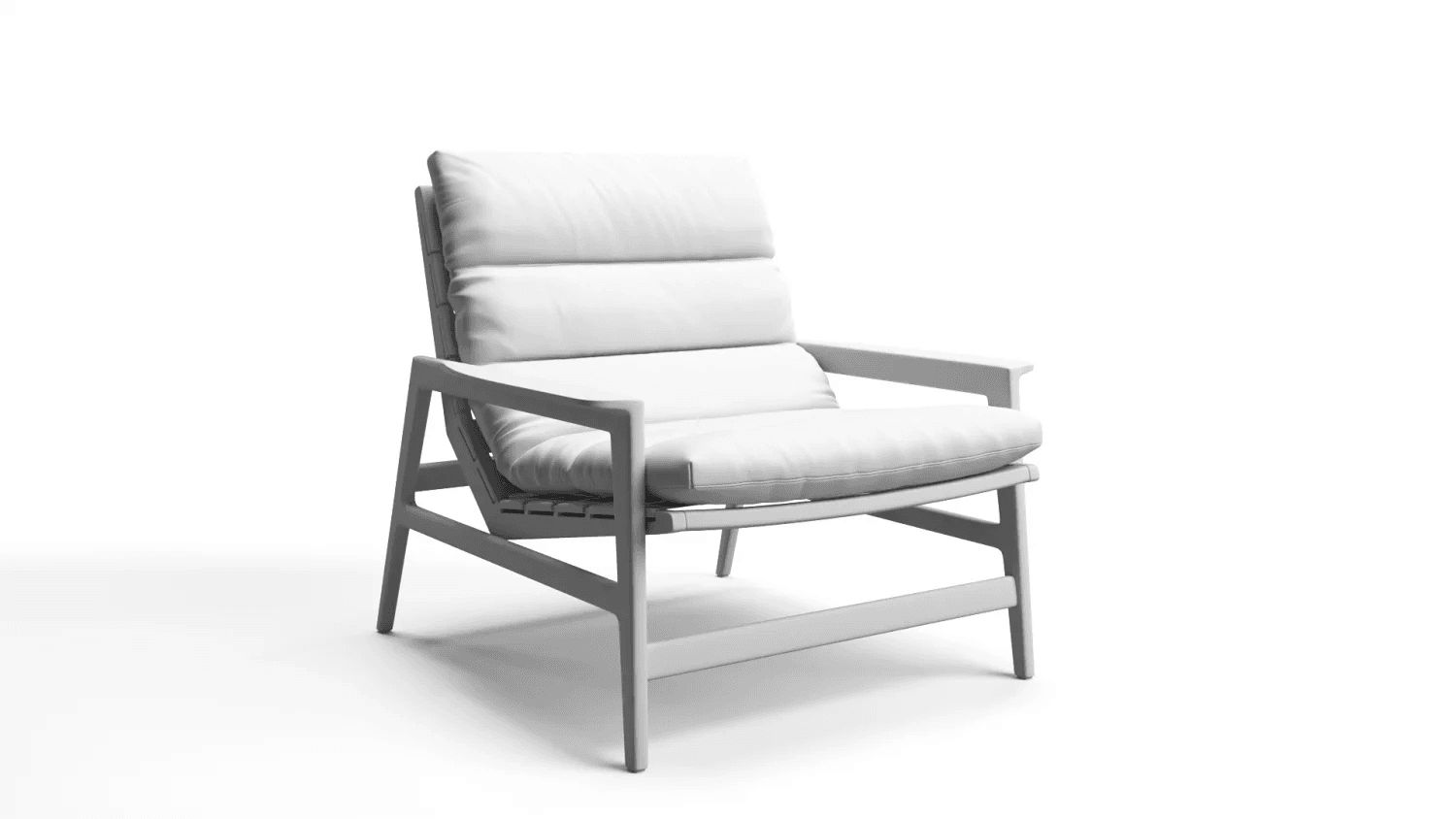

- Creating base shapes using high-poly or low-poly approaches
- Ensuring correct proportions based on dimensions
- Producing a gray (clay) model for early validation
- Adding secondary and tertiary details
Step 3: Applying Textures and Materials

- Using PBR workflow (albedo, roughness, normal, displacement)
- Matching fabrics, metals, wood, and plastics
- Reviewing samples and adjusting textures
Step 4: Rendering the Model on White Background
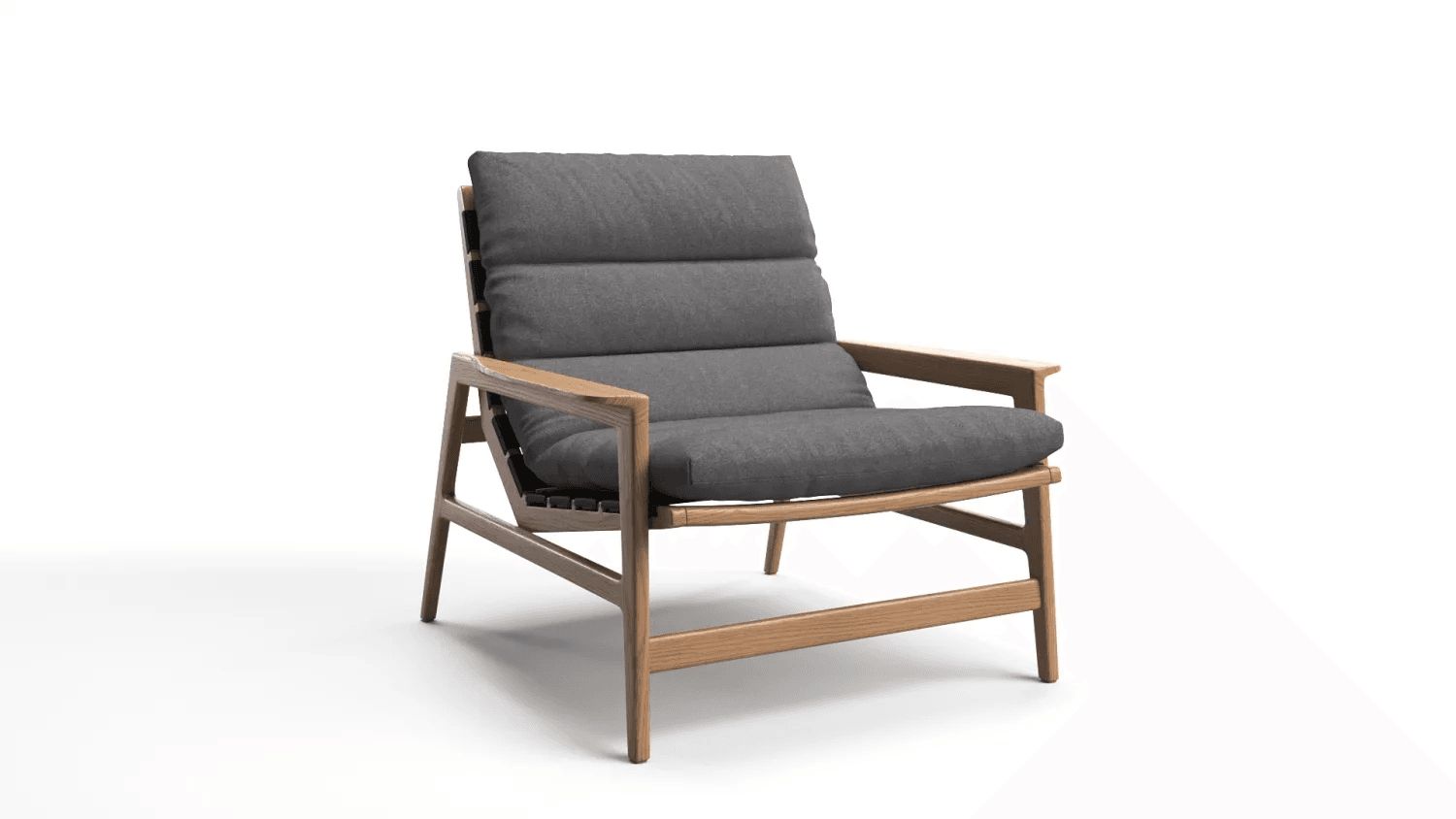

- Test renders to verify geometry
- Checking lighting to reveal imperfections
- Reviewing scale and proportions
Step 5: Post-production

- Fixing artifacts
- Color correction
- Final scale verification
- Preparing final deliverables
Software for 3D Modeling

Different tools are used for different tasks and object types.
A. Hard-Surface / Product Modeling
3ds Max
Industry standard for product visualization.
Blender
Versatile: modeling + retopology + unwrapping.
Fusion 360
Great for mechanical and engineered shapes.
SolidWorks / Rhino
Used for CAD and highly accurate industrial forms.
B. Organic and Fabric Modeling
ZBrush
Best for sculpting and complex decorative shapes.
Marvelous Designer
Realistic cloth and upholstery simulation.
Houdini
Procedural modeling; ideal for complex forms and fabric logic.
C. Models for Production / 3D Printing
• SolidWorks • Onshape • Inventor • CATIA Used when exact dimensions and NURBS geometry are required.
D. Real-Time, AR, Low-Poly Pipelines
• Blender • 3ds Max retopology tools • Instant Meshes • Simplygon Real-time models require polygon optimization, clean UVs, and lightweight topology.
Why software choice matters
• Hard-surface and organic modeling require different tools • CAD models need adaptation for visualization • Clean topology determines lighting quality and realism • Model type (render, AR, animation) dictates pipeline

Get the Commercial CGI & Product Rendering Guide for Marketing Directors
Everything you need to scale product content with CGI.
Get expert insights, real project examples, and strategies with proven ROI.
Fill out the form to receive the guide directly in your inbox.